bitesize games:
Fruit Drop
![]()
Explanation of Code!
You can copy these sprites or make your own! Make sure you draw each of these sprites in the exact same place as we do in the video, because the code will look for their sprite number. But once you understand the code, you can draw as many sprites as you want, where ever you want!
The first code we write at the top of the file are the variables. These help us set up the game and keep track of data.
basket_sprite=1
player_sprite=2
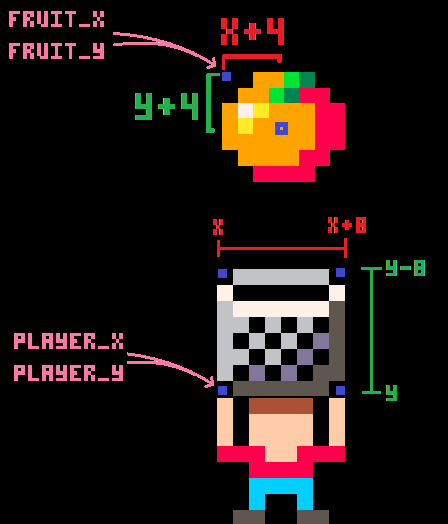
player_x=64
player_y=100The first two variables are named basket_sprite and player_sprite. Then the equals sign tells the game to remember it with whatever we write next. basket_sprite and player_sprite each hold a number and that number is the sprite # of the basket and player in the sprite sheet.
The next variables are named player_x and player_y. Together these tell the game where the player is on the screen. As the player moves, these numbers will change, but we can set the starting position here.
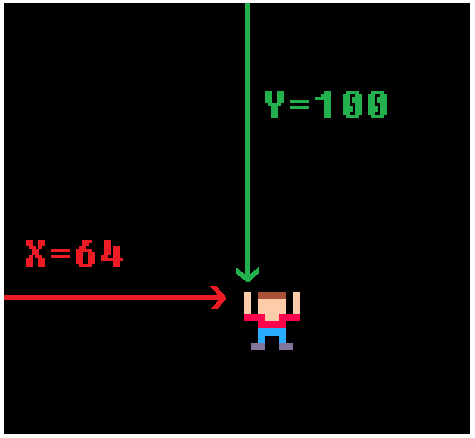
x = 64 because there are 128 pixels from left to right, so 64 is half, in the center.
y = 100 because there are 128 pixels from top to bottom, so 100 is near the bottom.
These will be used later to start the player in the center and near the bottom of the screen.
The next set of variables are for keeping track of the fruit data. The best way to do this is to use a table.
fruits={}
fruit_start=16
fruit_count=6
fruit_interval=16These {} are called "curly brackets" and normally look like this: { }
Curly Brackets are used to create TABLES. fruits={} creates an empty table. We will fill it later.
fruit_start is the sprite number of the first fruit.
fruit_count is the total number of fruit sprites.
fruit_interval is the number of pixels between each fruit.
We will use these to create the random fruit in the game.
The last set of variables are for keeping track of some game data.
gravity=1
level=1
points=0gravity is the speed that the fruit will fall by.
level is the number of fruit that fall. Each level adds more fruit.
points is the player's score, how many fruit you catch.
Next are the 3 basic functions that run the game.
function _init()
end
function _update()
end
function _draw()
end_init() sets up the game.
_update() makes changes to the game 30 times every second.
_draw() runs after _update and draws to the game screen, also 30 times every second.
![]()
Let's start by drawing the player on the screen.
function _draw()
cls()
rectfill(0,108,127,127,3)
spr(player_sprite,player_x,player_y)
spr(basket_sprite,player_x,player_y-8)
endcls() clears the screen.
rectfill() draws a rectangle that is filled with a color.
spr() draws a sprite.
The player is drawn as player_sprite, which we already set as 2. The player is drawn at player_x and player_y position on the screen.
If those variables change, this draw code will change with them! That's what variables are for!
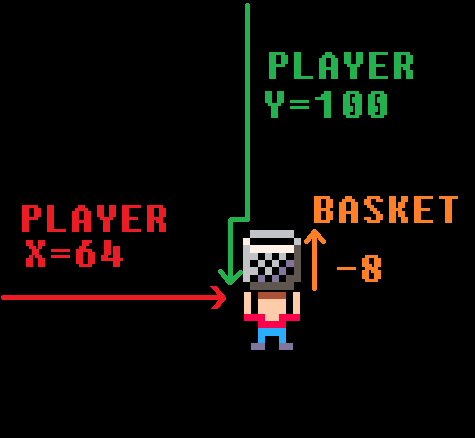
The basket is drawn as basket_sprite, which we already set as 1. The basket is also drawn at player_x and player_y position on the screen. But we want the basket to be above the player, so we just minus 8 pixels from player_y because the basket is 8 pixels tall.
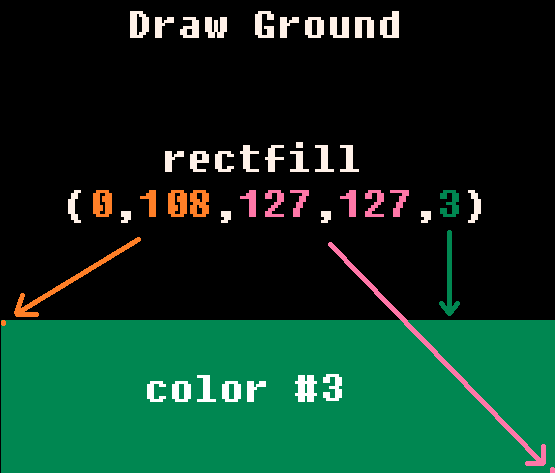
The ground is created by rectfill() which draws a filled rectangle. The first two numbers are the rectangle's X and Y COORDINATES at the top-left corner. The next two numbers are the rectangle's X and Y COORDINATES at the bottom-right corner. The last number is the COLOR NUMBER.
Next, we are updating the player controls!
function _update()
if btn(0) then player_x-=2 end
if btn(1) then player_x+=2 end
endbtn() (button) checks for a certain button that is pressed. pico-8 has 6 buttons, #0-5.
btn(0) checks for button LEFT.
btn(1) checks for button RIGHT.

To make the player sprite move based on the real player's controls, we just change the player_x and player_y variables up or down, and the sprite is drawn to match those changes.
In this game, the player only moves left and right, so only X changes and Y stays the same. If the player moves left, then the X should decrease (-) to a lower number. If the player moves right, then the X should increase (+) to a higher number.
Math time! Don't worry, it is simpler than it looks.
function _init()
for i=1,level do
fruit={
sprite=flr(rnd(fruit_count)+fruit_start),
x=flr(rnd(120)+5),
y=i*(-fruit_interval)
}
add(fruits,fruit)
end
endIn the set up of the game (the _init function), we will add fruit to the fruits table.
Each fruit will need a SPRITE number, an X coordinate, and a Y coordinate. Remember from when we drew the player sprite with SPR() that these three things are needed to draw any sprite to the screen.
First, we need to create a LOOP. This just repeats the same code a certain number of times so we don't have to copy paste code over and over again.
This is a FOR loop.
for i=1,level do
endi is a variable that is commonly used for a whole number that will count up or down. It counts the number of times this loop repeats.
i=1 sets the variable to start at 1, and it will automatically count up by 1 each time the loop repeats.
level is the variable we created at the top. We will use it to keep track of the levels in the game, as the game gets harder. We will use it here to tell this FOR LOOP when to stop repeating. The way the FOR LOOP works is, it will check if i is more than level, then the loop will not repeat anymore.
This is the code inside the loop that is going to repeat. Here's how we make many fruit!
fruit={
sprite= ,
x= ,
y=
}
add(fruits,fruit)fruit={...} starts a new table to hold data unique to each fruit: SPRITE #, X, and Y.
add(fruits,fruit) inserts into the fruits table, whatever data is held in fruit. We will be creating a table with other tables inside it! It sometimes gets confusing but it makes coding a lot easier! You'll see!
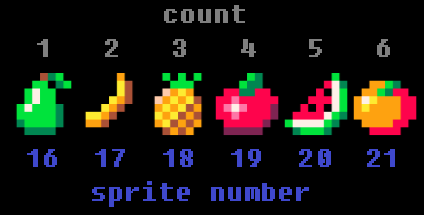
For the sprite number of each fruit we do:
flr(rnd(fruit_count)+fruit_start)flr() rounds a decimal down to the nearest whole number. Example: flr(4.6) rounds down to 4.
rnd() creates a random number between 0 and the number inside the ( ). Example: rnd(10) could be 0.4 or 9.345 but never more than 10.
rnd(fruit_count) means we want to get a random number between 0 and the total number of fruit.
But that will give us a number between 0 and 6, and we don't have fruit sprites in those low numbers. Our fruit sprites start at sprite number 16! So...
rnd(fruit_count)+fruit_start will take the random number between 0 and 6, then add 16 to it! Now we will get a number between 16 and 22!
Then we use flr() to round the random decimal number between 16 and 22 down to a whole number, so it gives one of these numbers: {16,17,18,19,20,21}, which will match the sprite number of a fruit!
For the X coordinate of each fruit we do:
flr(rnd(120)+5)rnd(120)+5 gets a random decimal number between 5 and 125.
This will position the fruit somewhere horizontally inside of the screen. And again, flr() will round down to make it a whole number.
For the Y coordinate of each fruit we do:
i*(-fruit_interval)i*(-fruit_interval) gives a number that is a certain amount less than the previous number.
Remember that i increases with each run of the FOR LOOP. So on the first run, i is 1, but on the second run, i is 2. So let's change those variables for the numbers they represent and show the math.
On the first loop: i=1 and fruit_interval=16
So i*(-fruit_interval) means 1 times -16 which equals -16
On the second loop: i=2 and fruit_interval=16
So i*(-fruit_interval) now means 2 times -16 which equals -32

So the first fruit in the table will be at Y (height) of -16 which is above the game screen. And the second fruit will be higher than that one, at -32. And the next fruit will be 16 pixels above the last one. On and on.
This is where we update all of the fruit.
function _update()
for fruit in all(fruits) do
end
endfor fruit in all(fruits) is a special TABLE loop.
This will repeat over each item inside of the table we give it, which is: fruits. It also sets the item it is currently on as a variable we set, which we named: fruit.
But if you remember, each item in the fruits table, is also a table! Don't worry, this is where tables shine at holding lots of data.
This is what the fruits table looks like with each item as a table named fruit.
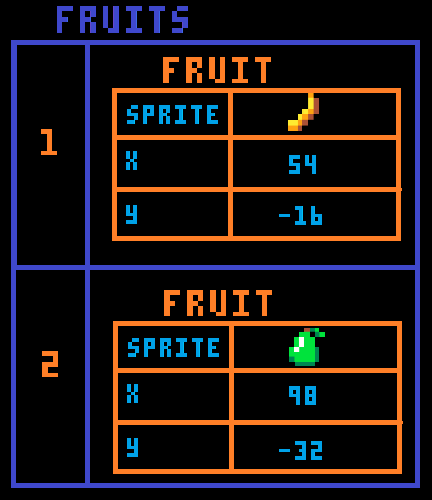
The first thing we want to update about the fruit is to make them fall down the screen. So that means changing their Y, by adding to it. So inside of our table loop:
fruit.y+=gravityfruit.y is how we access the data inside the inner table.
+=gravity means add to the number it already is by the number set in the variable gravity.
So let's take the table in the picture as an example. The first fruit is a banana, with a Y of -16. And remember the gravity that we set is 1. So fruit.y+=gravity just means -16+1. And it will update this 30 times a second because of _update(). So every update the banana will move 1 pixel down the screen, and after 1 second, the banana will have moved 30 pixels!
With this set up, the higher you set the gravity, the faster the fruit will fall! Try it out!
The next code inside of this table loop detects if the fruit fall into the basket!
if fruit.y+4>=player_y-8
and fruit.y+4<=player_y
and fruit.x+4>=player_x
and fruit.x+4<=player_x+8 then
points+=1
del(fruits,fruit)
endThis type of code is basic "collision detection". In other words, checking if one thing hits another. In this case, we want to know if the middle of the fruit is within the limits of the basket.
fruit.y+4 and fruit.x+4 tell us the middle of the sprite because we know that the fruit are each 8 pixels wide and tall.
player_x and player_y help us create limits, which is a box (a hitbox!) to compare the fruit position with to know if the fruit is inside of it.
If that is true, then the fruit IS inside the basket, so we increase the player's points and delete that fruit.
points+=1 will take whatever the points is and increase it by 1.
del() deletes an item from a table.
del(fruits,fruit) deletes from the fruits table, the current item we are looping on: fruit.
The last thing inside of this table loop deletes fruit that hit the ground.
if fruit.y>100 then
del(fruits,fruit)
endIf the Y of the fruit is more than 100 (about where the ground is) then delete that fruit from the fruits table.
We are done with the table loop. But the last thing we need to update is when there are no more fruit in the game, then we increase the level and reset the fruit table.
if #fruits==0 then
level+=1
_init()
end# (#) counts the items in a table.
if #fruits==0 checks if the number of items in the fruits table is 0. In other words, if the fruits table is empty, and there are no more fruit in the game.
level+=1 takes whatever number level is and increases it by 1.
_init() triggers the code inside the function named _init. That is the code that creates fruit and puts them in the fruits table. Since we just increased the level, when we run that code again, the number of fruit put in the game will also increase.
LAST THING TO DO!!!!
function _draw()
--after drawing ground and sprites--
for fruit in all(fruits) do
spr(fruit.sprite,fruit.x,fruit.y)
end
print("score= "..points)
endfor fruit in all(fruits) do is the same table loop we used in _update to repeat over each fruit.
spr(fruit.sprite,fruit.x,fruit.y) draws the sprite#, X, and Y of the fruit that is currently selected by the table loop.
print() writes to the game screen.
print("score=") writes the exact characters inside the " ", called a STRING.
.. will combine (CONCATENATE) two things next to each other.
print("score="..points) writes on the screen: the STRING "score=" then the number held by the variable points.
Well done! That's everything you need to know about how this game code works! Now test your understanding by playing the game and changing the code to make it your own! Have fun!
basket_sprite=1
player_sprite=2
player_x=64
player_y=100
fruits={}
fruit_start=16
fruit_count=6
fruit_interval=16
gravity=1
level=1
points=0
function _init()
for i=1,level do
fruit={
sprite=flr(rnd(fruit_count)+fruit_start),
x=flr(rnd(120)+5),
y=i*(-fruit_interval)
}
add(fruits,fruit)
end
end
function _update()
if btn(0) then player_x-=2 end
if btn(1) then player_x+=2 end
for fruit in all(fruits) do
fruit.y+=gravity
if fruit.y+4>=player_y-8
and fruit.y+4<=player_y
and fruit.x+4>=player_x
and fruit.x+4<=player_x+8 then
points+=1
del(fruits,fruit)
end
if fruit.y>100 then
del(fruits,fruit)
end
end
if #fruits==0 then
level+=1
_init()
end
end
function _draw()
cls()
rectfill(0,108,127,127,3)
spr(player_sprite,player_x,player_y)
spr(basket_sprite,player_x,player_y-8)
for fruit in all(fruits) do
spr(fruit.sprite,fruit.x,fruit.y)
end
print("score= "..points)
end

Garbage Collector by Luna Forever
This variant of Fruit Drop is a great example of how you can change the theme and sprites of the game, and add multiple scenes like a main menu and game over scene. It also adds music, a high score tracker, health for the player, and dangerous spikes that you must avoid.
Hungry Potato by voidgazerBon
This variant of Fruit Drop takes the game very far with an animated background, flying and walking enemies, player health, jump physics, custom cover art, and even a boss fight!![]()
15002
6 May 2020